THE FUTURE OF MAKING | 3D PRINTING
Additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing is one of the prominent technologies shaping The Future of Making.
THE FUTURE OF MAKING | 3D PRINTING
Additive manufacturing is one of the prominent technologies shaping The Future of Making.
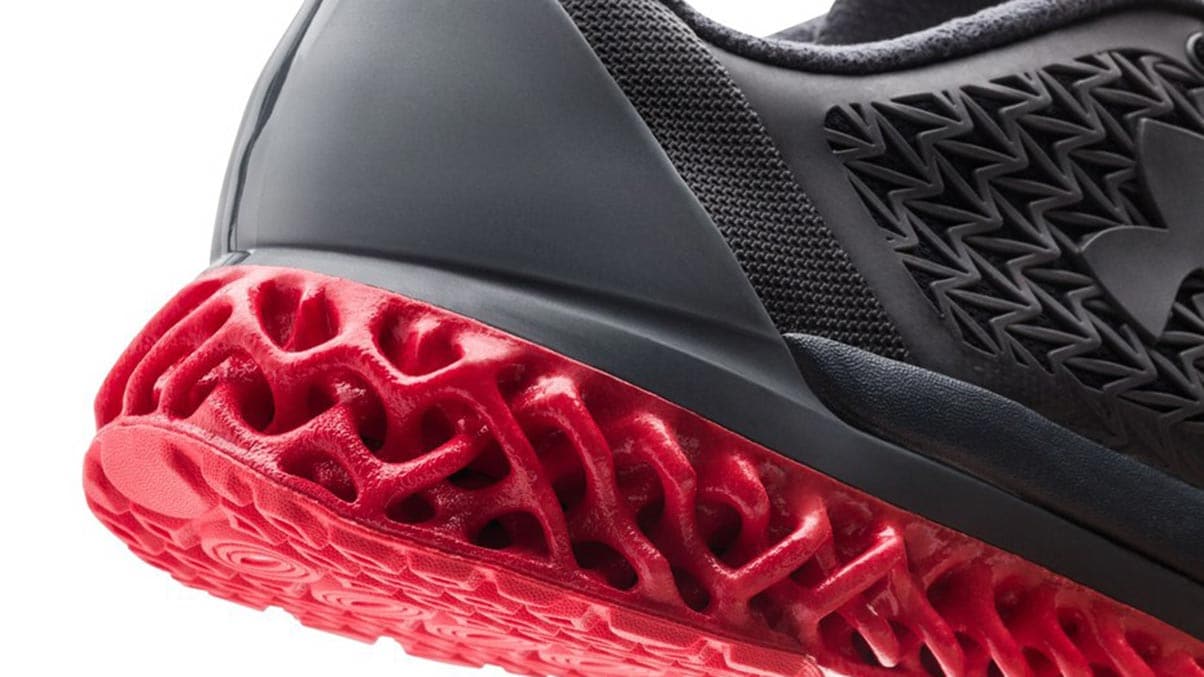
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a process used to create a physical (or 3D) object by layering materials one by one based on a digital model. Unlike subtractive manufacturing that creates its final product by cutting away from a block of material, additive manufacture adds parts to form its final product.

Additive manufacturing is primarily used by engineers, architects, and construction managers, and has replaced manual drafting. It helps users create designs in three dimensions to visualize construction, and enables the development, modification, and optimization of the design process. This process helps engineers make more accurate representations and modify them more easily to improve design quality.

One of the earliest ways to use additive manufacturing for industrial purposes, this practice is now becoming an industry standard. CAD-to-additive simulation technology is improving exponentially, helping accelerate the production of lightweight components.

The capability to customize and tailor products helps manufacturers quickly create and deliver custom solutions to clients.

While prototyping is the original use of additive manufacturing, many companies are now delivering reliable 3D-printed finished goods in both commercial and industrial applications.
Additive manufacturing can encompass multiple processes, depending on the hardware, material requirements, and product application.

A vat of photopolymer liquid is cured by focused UV light that builds parts layer by layer for a high-detail surface finish.

A powder substrate is hardened when the printing head deposits a drop of binding fluid in a layering process. Includes full-color prototype fabrication.

Used where surface finish and form testing are needed; a printhead lays down successively solidifying layers of UV curable material to form prototyped designs.
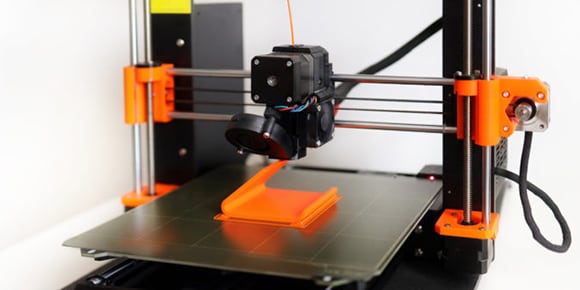
Fused deposition modeling is a common 3D printing process in which a heated nozzle extrudes a plasticized material to form products from a sliced CAD model.
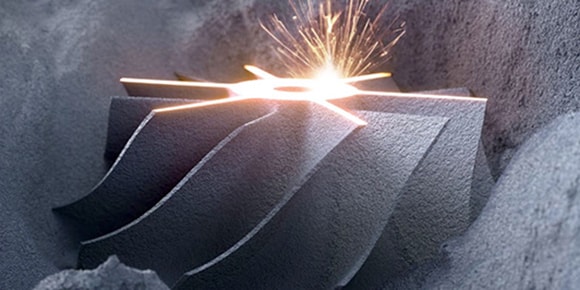
Laser or electron beams rapidly fuse layered powder material, such as various metals, together. This technique is used for circuits, structures, and parts.

Ribbons of metal or paper are bonded through ultrasonic welding or adhesive, respectively; the finished shaping is completed through further material removal processes.

Repairs or adds to existing components by using a multi-axis nozzle to extrude laser-melted material, commonly metal powders, onto the printing surface.

Using generative design and simulation software to produce complex metal parts helps manufacturers get more value from proven metal casting processes.
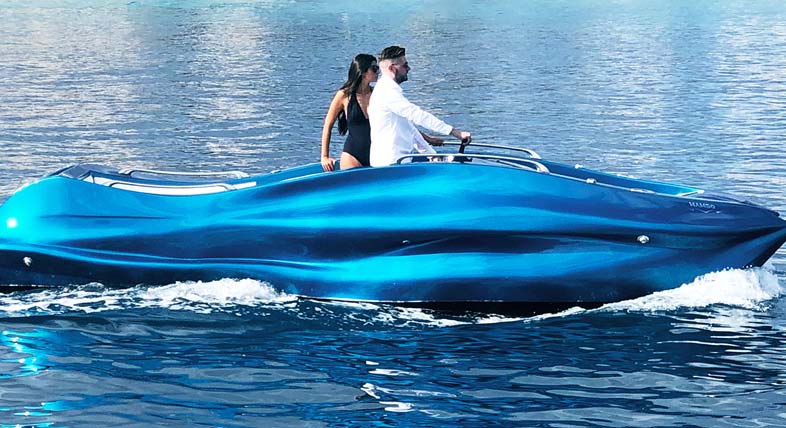

Large scale printing
Moi Composites created a 3D-printed boat design that would have been inconceivable to produce using traditional boatbuilding fabrication methods.
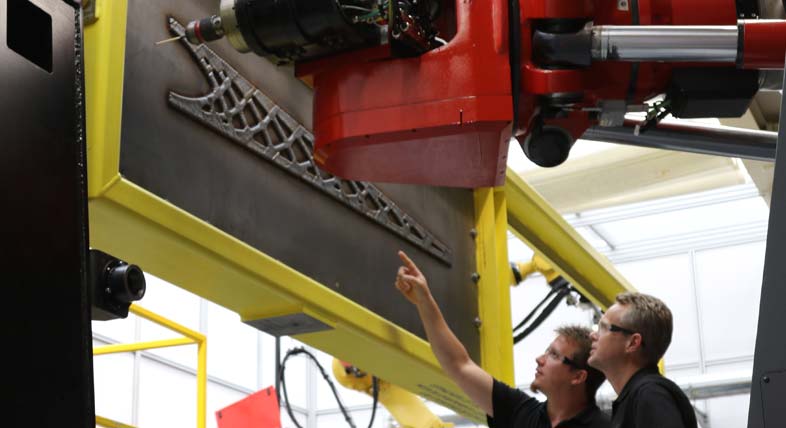

Transforming Construction
LASIMM was developed to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and offer production flexibility, which are Europe’s core pillars to improve industrial competitiveness.
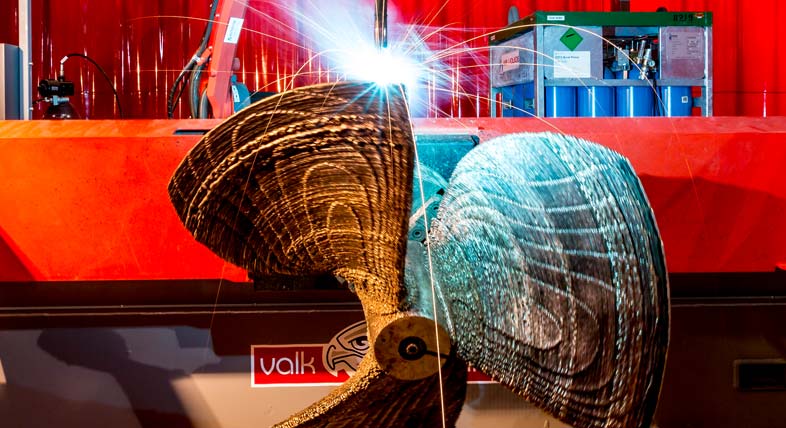

3D printed propeller
Port of Rotterdam's RAMLAB and Autodesk produce the world's first class certified 3D printed ship propeller.
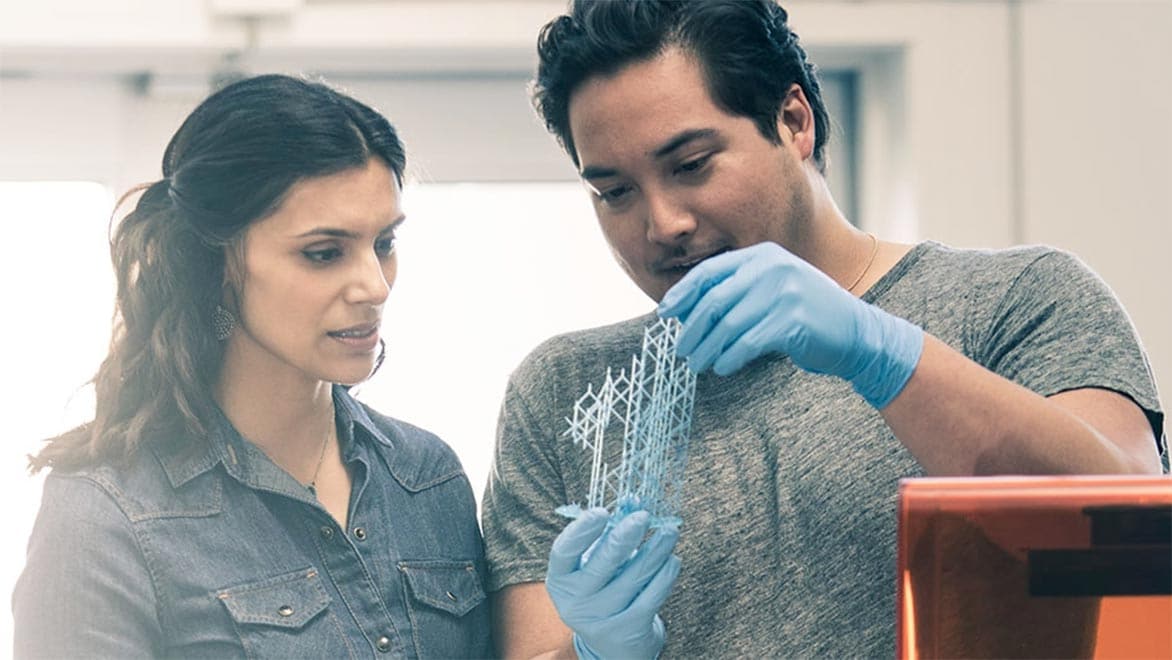

Additive engineering is evolving at a rapid pace. 3D printing now involves metal laser sintering, powder bed fusion, and even hybrid techniques involving casting and robotics.
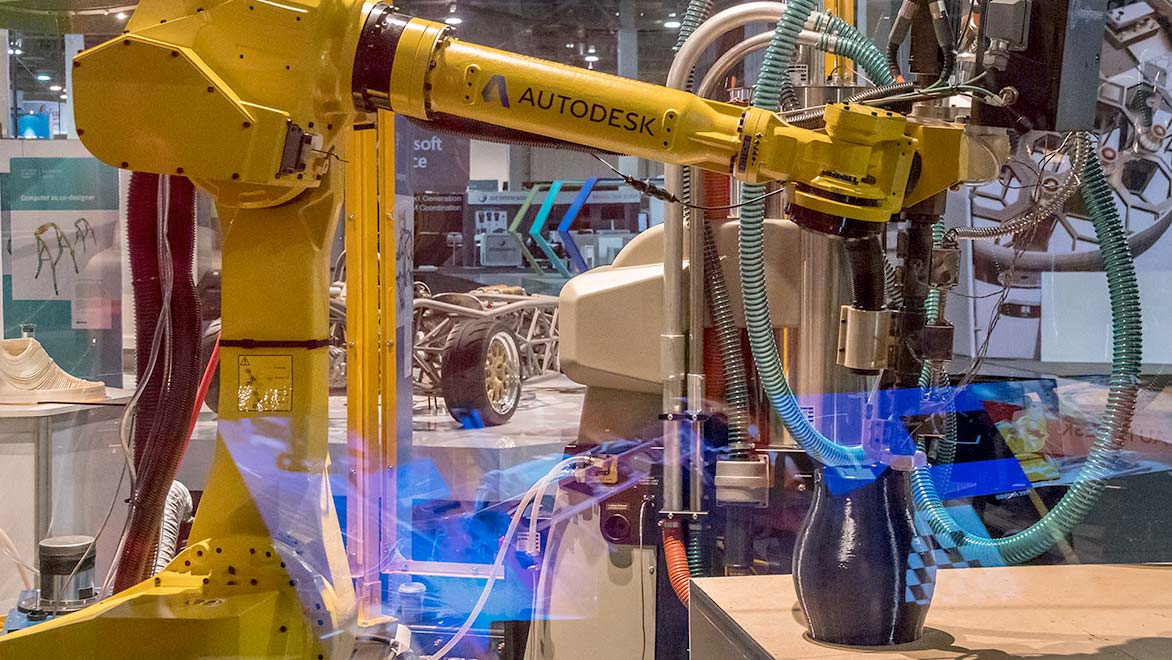

Additive manufacturing has evolved rapidly in recent years. It has been embraced by major industrial companies looking for ways to improve their products. The ability to deliver near-instant parts production and fully custom designs that cannot be replicated with other manufacturing techniques has accelerated investment and research in additive engineering.
Learn more about additive manufacturing with these blogs, guides, tips, and tutorials.
Learn from our experts, sharpen your skills, and see what’s possible with Autodesk software.
Get the engineer’s guide to understanding and implementing additive manufacturing in the production process.
Make the most out of your Netfabb subscription using these tips, tutorials, and free resources.
Begin learning additive manufacturing to take your ideas from concept to construction.
Experience the power of cloud-based 3D CAD. Master 3D modeling and 3D printing with beginning and advanced tutorials.
Get shortcut keys and commands lists for popular Autodesk products.
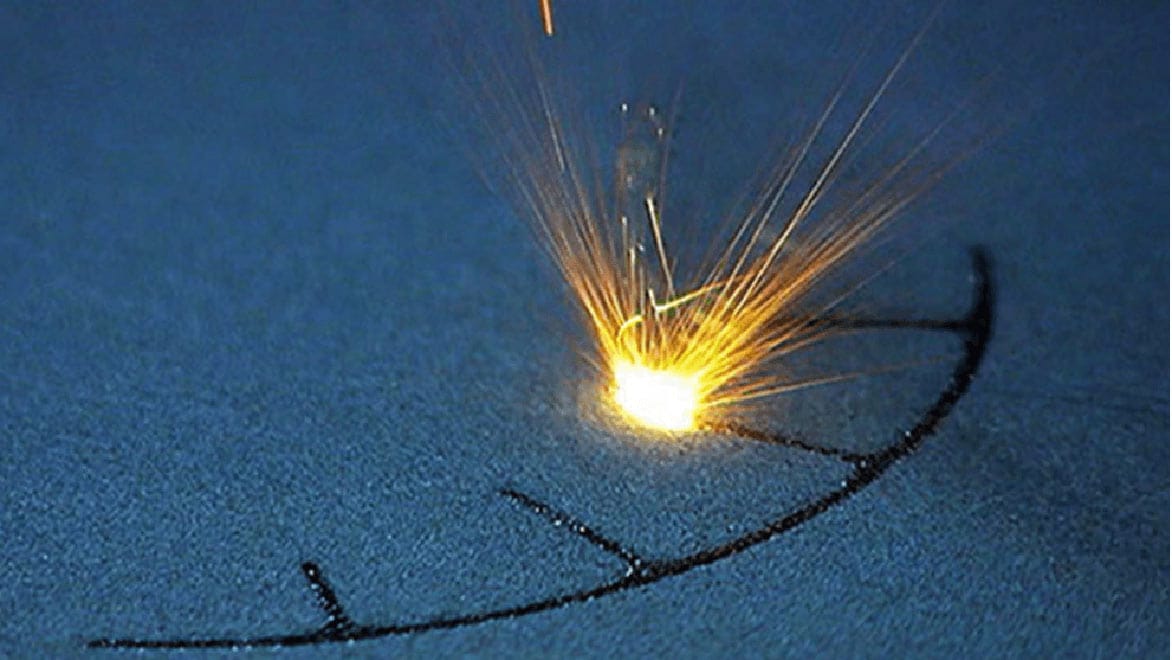

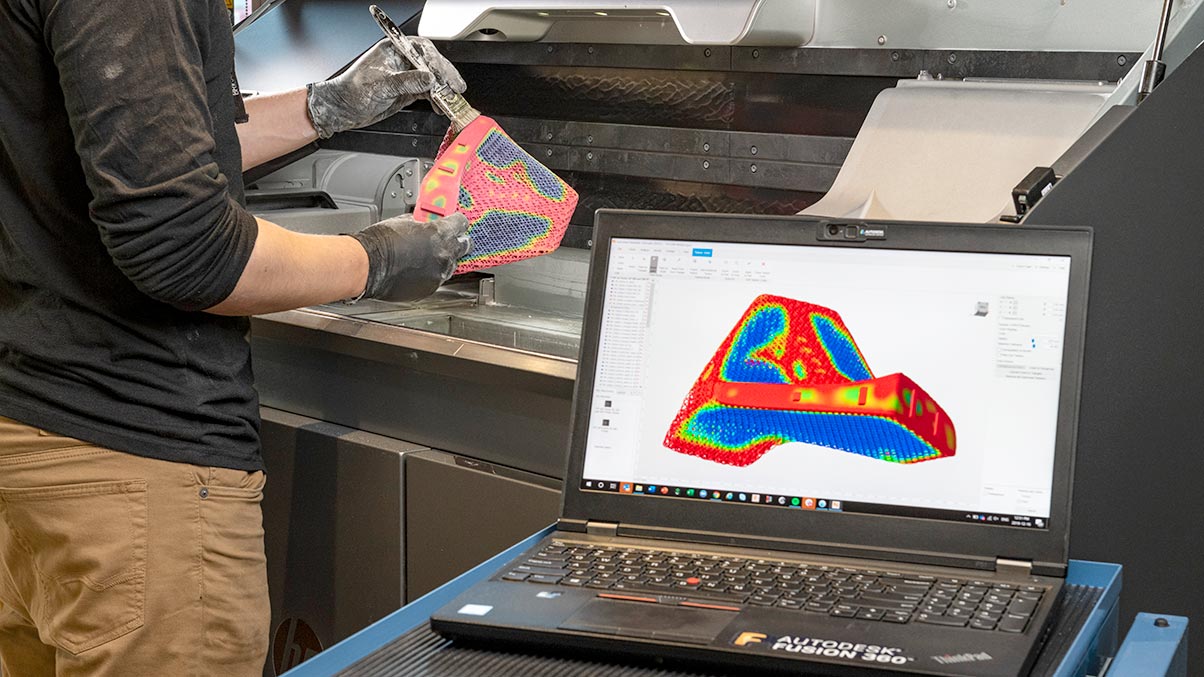
The Fusion 360 Additive Build Extension allows you to select 3D print parameters, automatically orient parts, and generate fully associative support structures for efficient programming. You can also quickly create subtractive finishing operations within the same Fusion 360 environment to machine precise features and achieve a high-quality surface finish.
Below you will find answers to the questions we get asked the most about additive manufacturing and Autodesk’s software.
Additive manufacturing is used to produce lighter, stronger parts and systems with much greater efficiency. It has uses across a variety of industries including:
Additive manufacturing provides a number of advantages for industrial use. Significantly, Additive technologies produce parts that are lighter, stronger and faster to create than their traditional counterparts.
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is the process of adding material to create an object. Machines deposit material, layer upon layer, in precise geometric shapes, and Computer-aided-design software or 3D object scanners are used to create models to direct the hardware.
A variety of materials are used in additive manufacturing, including metals, ceramics, and glass. Each material has its own advantages and applications. Powders for 3D printing metals can range from titanium to alloys, to precious metals such as gold. Polymers (including ABS, PLA, PVA and polycarbonate) and metals (gold, stainless steel, silver, steel, titanium) are two of the most commonly used materials. There are many other materials which can also be used, including ceramics, glass, resin, and potentially even human cells.
3D printing is a more consumer-friendly phrase, and it’s becoming more and more popular in use than additive manufacturing. There are some subtle differences, however, and the term “additive manufacturing” can be used to refer to other processes such as rapid prototyping, whereas 3D printing is more restrictive.
The two phrases can best be defined as:
The technology offers many advantages over traditional manufacturing methods, such as flexibility, speed and cost reduction. As additive manufacturing is by definition an additive method, there is far less waste. Any powder left over in the machine can be reused for the next project, so nothing needs to be tossed or scrapped. Conventional methods are subtractive (removing material to get the final result), which can result in up to 90% of material ending up as waste. Additionally, the precision which can be offered means that quality is higher, and overall production times are reduced. Lastly, the flexibility over the design means there’s no need to have a “one size fits all” approach, resulting in more cost-effective processes.