Justin Matejka, Michael Glueck, Tovi Grossman, George Fitzmaurice
The Effect of Visual Appearance on the Performance of Continuous Sliders and Visual Analogue Scales
Best Paper Award Winner
ACM SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems
2016
The Effect of Visual Appearance on the Performance of Continuous Sliders and Visual Analogue Scales (2:22 min.)
Abstract
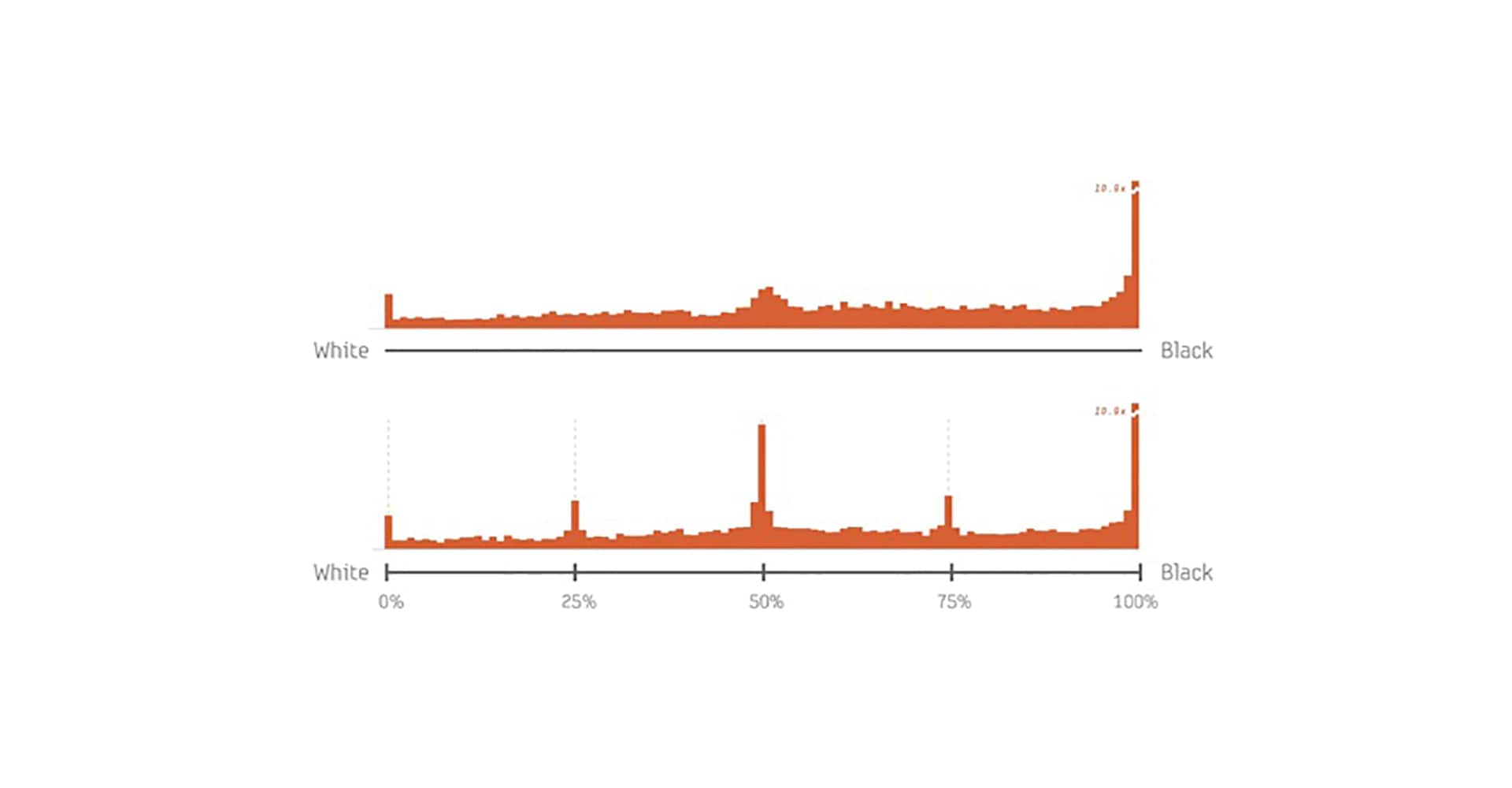
Sliders and Visual Analogue Scales (VASs) are input mechanisms which allow users to specify a value within a predefined range. At a minimum, sliders and VASs typically consist of a line with the extreme values labeled. Additional decorations such as labels and tick marks can be added to give information about the gradations along the scale and allow for more precise and repeatable selections. There is a rich history of research about the effect of labelling in discrete scales (i.e., Likert scales), however the effect of decorations on continuous scales has not been rigorously explored. In this paper we perform a 2,000 user, 250,000 trial online experiment to study the effects of slider appearance, and find that decorations along the slider considerably bias the distribution of responses received. Using two separate experimental tasks, the trade-offs between bias, accuracy, and speed-of-use are explored and design recommendations for optimal slider implementations are proposed.
Related Publications
Loading...
Related Projects
-

Visualization & Visual Analytics
Visual data representations leverage the power of human perception to process complex information, and through interaction, garner new insights. Our research focuses on visualizing data from a wide variety of domains and fundamentally tackles the question, what makes a visualization effective? We explore novel visual encodings and interaction techniques, multiscale approaches, and even simulation to bridge human and automated analysis of multivariate, time-series, and graph data, ultimately aiding in hypothesis generation, testing, and sense making.
-
-